Technological advancements have given rise to fascinating concepts and materials that are shaping the future. Two such innovations are Electromagnetic Fields (EMF) and Carbon Nanofibers (CNF). Though they differ in nature and function, they hold individual significance in science and technology while also presenting opportunities for overlap in cutting-edge applications. This article dives into both topics, exploring their definitions, uses, and potential challenges.
What Are Electromagnetic Fields (EMF)?
Electromagnetic fields are invisible areas of energy resulting from the motion of electric charges. They are categorized into two types:
- Low-frequency EMF – Found in household appliances, power lines, and electrical wiring.
- High-frequency EMF – Includes radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays, often associated with telecommunications, medical imaging, and industrial applications.
EMF plays a vital role in various technologies. For instance, radio waves facilitate wireless communication, while microwave radiation powers devices like radar systems and ovens.
Applications of EMF
- Telecommunications: Mobile phones, Wi-Fi networks, and satellite communication systems rely on EMF to transmit data over long distances.
- Medical Technology: MRI machines employ magnetic fields to create detailed images of the human body, aiding in diagnostics and research.
- Clean Energy: Electromagnetic induction underpins devices like transformers and generators, essential for electricity production and grid integration.
Challenges of EMF
The primary challenge associated with EMF lies in its potential impact on human health and the environment. Prolonged exposure to high-frequency fields has raised concerns, though extensive research continues to assess and address these risks.
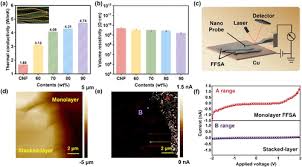
What Are Carbon Nanofibers (CNF)?
Carbon Nanofibers are cylindrical structures composed of layers of graphene arranged in nanometer scales. Their unique properties—such as high strength-to-weight ratio, electrical conductivity, and thermal resilience—make CNF a revolutionary material in nanotechnology and manufacturing.
Applications of CNF
- Aerospace and Automotive: CNF enhances lightweight composite materials, leading to fuel-efficient vehicles and robust spacecraft.
- Energy Storage: Carbon nanofibers serve as electrodes in batteries and supercapacitors, enabling efficient energy storage solutions.
- Medicine: CNF-based scaffolds are used in regenerative medicine for growing tissue and repairing injuries, thanks to their biocompatibility.
Challenges of CNF
While CNF holds immense potential, its production is energy-intensive and costly. Additionally, the environmental and health impacts of large-scale CNF usage remain under investigation, particularly in terms of nanoparticle exposure.
How EMF and CNF Connect
Although EMF and CNF might seem unrelated at first glance, they intersect in a number of emerging technologies:
- Advanced Sensors: CNF’s conductive properties could be integrated into EMF-sensitive devices to create highly efficient sensors for environmental monitoring or industrial control systems.
- Wireless Energy Transfer: The development of CNF-enhanced electromagnetic receivers could facilitate more effective wireless charging systems for electronics and vehicles.
- Electronics Miniaturization: By combining CNF materials with EMF technology, next-generation electronic components can achieve unprecedented performance in compact designs.
The Future Outlook
The combination of EMF and CNF represents a promising frontier for scientific and technological innovation. Whether improving healthcare, energy solutions, or communication networks, these advances could transform industries. However, as we harness their potential, it’s essential to address challenges such as health concerns, production costs, and environmental impact through continued research and ethical practices.
By better understanding EMF and CNF, we gain insight into the possibilities that lie ahead in science and technology. These groundbreaking concepts remind us of the importance of innovation in building a sustainable and efficient future.